An infectious disease can be transmitted via different vehicles. Bodily fluids, contaminated food or water sources, animals, and other humans can all participate in passing along an infectious disease to its next host. Infectious diseases are caused by organisms transmitted such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites through direct and indirect contact. Disease-causing organism symptoms can range from general signs to immediate medical assistance needed.
Certain bacteria can release toxins into your system to cause sickness. Viral infections can get within a cell to duplicate themselves, causing an increase in toxic reproduction. Fungal infections become hazardous when harmful fungi get overgrown or sink themselves into openings within the skin or body. Parasites use the body to live, increasing harm through swift reproduction.
Some infectious diseases can be passed from person to person, through insects or animals, and contaminated food or water. Depending on the infectious organism, signs and symptoms may vary. Mild infections may show fever and fatigue, while some life-threatening infections may need hospitalization. The nose, mouth, and skin are common places for disease pathogens to enter.
A variety of agents can invade the body, but symptoms develop when cells are damaged or destroyed by the increased contamination of infectious cells. Some general signs of common infectious diseases include:
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Sore throat
- Coughing and nasal congestion
- Muscle Aches
- Diarrhea
- Chills and sweats
Individuals with a weaker immune system are more susceptible to an increased risk of contracting an infectious disease. People at a higher risk of infection due to a weaker immune system could be children, adults over 50, unvaccinated individuals, healthcare workers, and those traveling to highly concentrated animal and bug disease-carrier countries.
The first line of defense when blocking pathogens from entering the body is personal hygiene. Good hygiene habits avoid the spread and prevention through several measures. Depending on the infectious disease, your plan of action will vary.
Common preventative measures include:
- Vaccination, when available
- Regular, thorough handwashing
- Proper donning of high-quality protective clothing
- Distancing during work and personal activities
- Wearing the correct respiratory protection
- Utilization of appropriate disinfectants on commonly used surfaces
For more information, we encourage you to visit the CDC website for the most up-to-date recommendations.
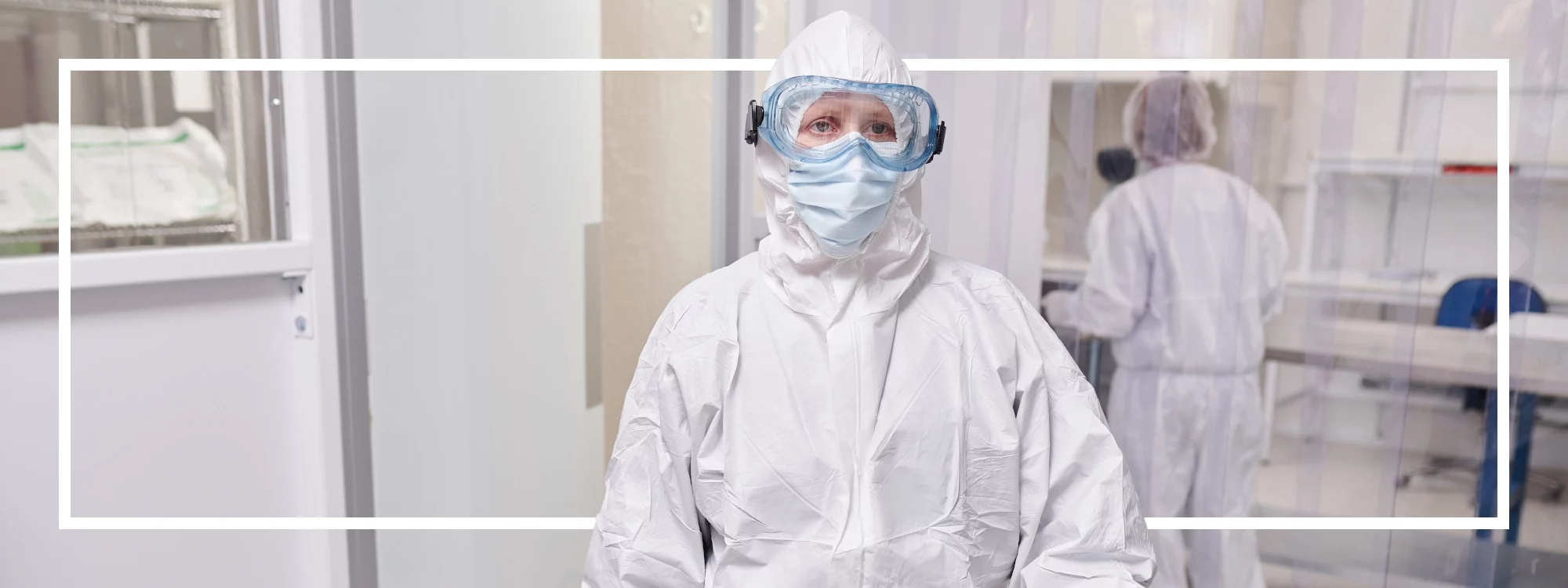
If you work in an environment where you are exposed to deadly infectious diseases, it’s important to understand how that particular agent can spread and what protective clothing can help protect you from infection.
We suggest looking for PPE that is certified to EN 14126, which contains four tests to measure protective workwear fabric against contaminated pressurized liquids, contaminated dry particulates, contaminated surfaces, and more. However, the standard only requires that a garment is tested using one method, so it’s important to know what hazard you are dealing with.
If you have questions about the right protective workwear for your environment, one of our representatives would be happy to offer some assistance.